1、Hive的DDL语法操作
1.1、Hive数据库DDL操作
(1)创建数据库create database db_hive2;或者create database if not exists db_hive;
数据库在HDFS上的默认存储路径/user/hive/warehouse/*.db
(2)显示所有数据库show databases;
(3)查询数据库show database like ‘db_hive’;
(4)查询数据库详情desc database db_hive;
(5)显示数据库desc database extended db_hive;
(6)切换当前数据库use db_hive;
(7)删除数据库
#删除为空的数据控drop database db_hive;
#如果删除的数据库不存在,最好采用if exists判断数据库是否存在drop database if exists db_hive;
#如果数据库中有表存在,需要使用cascade强制删除数据库drop database if exists db_hive cascade;
1.2、Hive表的DDL操作
1.2.1、建表语法介绍
1 | CREATE [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name` |
字段解释说明:
1 | CREATE TABLE :创建指定名称的表,如果存在报异常,可以使用 IF NOT EXISTS :来避免这个异常。` |
1.2.2、创建内部表
1、直接使用标准的建表语句:
1 | create table if not exists student11(` |
使用文本data.txt
1 zhang
2 lisi
2、查询建表法:
通过AS查询语句完成建表:将子查询的结果存放在新表里,有数据
1 | create table if not exists student1 as select id,name from student; |
3、like建表法:
根据已存在的表结构创建表
1 | create table if not exists student2 like student; |
4、查询表的类型:
1 | desc formatted student; |
5、内部表的默认位置:
(根据自己情况来定)
/user/hive_remote/warehouse/db_hive.db
6、将数据导入到Hive表中:
举列子:student11s是Hive表
1 | load data local inpath '/opt/bigdata2.7/hivedata/student.txt' into table student11; |
1.2.3、创建外部表
注意:default是数据库的名
1 | create external table if not exists default.emp(` |
创建外部表的时候需要加上external关键字,location字段可以指定,也可以不指定,不指定的话就是使用默认目录/user/hive/warehouse
1.2.4、内部表与外部表相互转换
1、内部表转换为外部表
#把student 内部表改为外部表
1 | alter table student set tblproperties('EXTERNAL'='TRUE'); |
2、外部表转换成内部表
1 | alter table student set tblproperties('EXTERNAL'='FALSE'); |
1.2.5、内部表与外部表区别
1、建表语法不同:
外部表建表的时候需要加上external关键字
2、数据存储位置不同:
创建内部表的时候,会将数据移动到数据仓库指向的路径;若创建外部表,仅仅记录数据所在的路径,不对数据的位置进行任何改变。
2、删除表之后:
内部表会删除元数据,删除表的数据。
外部表删除之后,仅仅是把表的元数据删除了,真实的数据还在,后期还可以恢复出来。
1.3、Hive表DDL语法经典案列
1.3.1、电影案列分析
1、数据格式:
1 | 战狼1,吴京1:吴刚1:小明1,2017-08-01 |
2、建表语句:
1 | create table t_movie(movie_name string,actors array<string>,first_date string)` |
3、导入数据:
确保hadoop用户对该文件夹有读写权限。load data local inpath '/opt/bigdata2.7/hive/movie';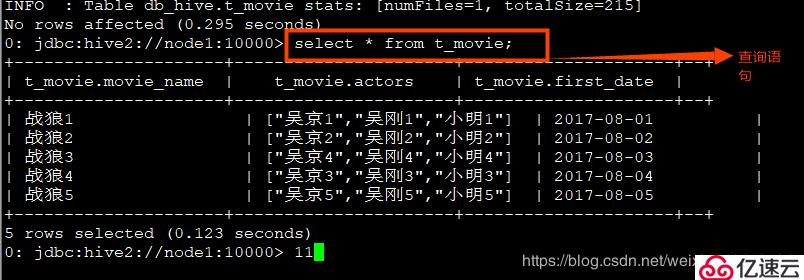
4、查询每个电影的第二个主演:
1 | select movie_name,actors[1] from t_movie; |
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-hgfz0RZZ-1579482997640)(2%E3%80%81Hive%E7%9A%84DDL%E8%AF%AD%E6%B3%95%E6%93%8D%E4%BD%9C.assets/image-20200109093038358.png)]
5、查询每部电影有几名主演:
select movie_name,size(actors) as num from t_movie;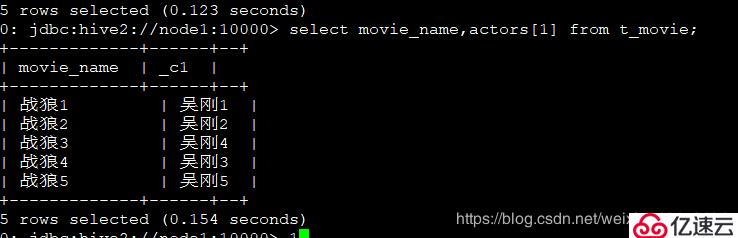
6、主演里包含吴刚5的电影
select movie_name,actors from t_movie where array_contains(actors,'吴刚5');
解析:
这里我们首先看到比较特殊的是主演的名字,而名字有都是string类型的,所以考虑到使用array类型,以为array存储的都是想同类型的元素。这里我们要使用collection items terminated by ‘:’,来设置指定复杂元素数据类型中元素的分隔符。
需要注意的是:collection items terminated by不仅是用来分隔array的,它的作用是分隔复杂数据类型里面的元素的。size内置函数是用来判断array元素的个数,array_contains()是判断array是否有这个元素。
1.3.2、个人档案型数据建表案例:
1、数据格式:
1,张三,18:male:北京
2,李四,19:male:南京
3,王五,20:male:上海
4,哈哈,18:male:北京
5,嘿嘿,12:male:成都
6,嘻嘻,14:male:济南
7,张丽,17:male:深圳
8,李物,19:male:重庆
2、建表语句:
1 | create table t_user(id int,name string,info struct<age:string,sex:string,addr:string>)` |
3、导入数据:
load data local inpath '/opt/bigdata2.7/hive/user' into table t_user;
4、 查询每一个人的id,名字,居住地址:
select id,name,info.addr from t_user;
解析:
这里比较特殊的字段是18:male:北京,对应的是年龄:性别:地址,每一个都有特殊的含义,我们考虑到无法构成一个键值对,所以map不合适,array只能包含相同的元素,而年龄是int类型,地址是strin类型,所以array不合适,所以考虑struct。
1.3.3、家庭档案数据建表案列
1、数据描述:
1,小明,father:张三#mother:李丽#brother:小刚,28
2,小鸿,father:李四#mother:王丽#brother:小志,28
3,小鹏,father:张物#mother:李美#brother:小英,28
4,张飞,father:张五#mother:李影#brother:小全,28
2、建表语句:
1 | create table t_family(id int,name string,family_mem map<string,string>,age int)` |
3、导入数据:
load data local inpath '/opt/bigdata2.7/hive/family' into table t_family;
4、查看每个人的父亲:
select name,family_mem["father"] from t_family;
5、查看有哪些亲属关系:select name,map_keys(family_mem),age from t_family;
6、查出每个人的亲人名字:
select name,map_values(family_mem) as relations,age from t_family;
7、查出每个人亲人的数量:
1 | select id,name,size(family_mem) as relation_num,age from t_family; |
2、Hive的DML语法操作
2.1、修改表的结构
2.1.1、修改表的名称
1 | alter table student_partition1 rename to student_partition2 |
2.1.2、表的结构信息
1 | desc student_partition3; |
2.1.3、增加/修改/替换列
增加列:
1 | alter table student_partition3 add columns(address string); |
修改列:
1 | alter table student_partition3 change column address address_id int; |
替换列:
1 | alter table student_partition3 replace columns(deptno string,dname string,loc string); |
2.1.4、增加/删除/查看表的分区
1、添加分区:
(1)添加单个分区:
1 | alter table student_partition1 add partition(dt='20170601'); |
(2)添加多个分区:
1 | alter table student_partition1 add partition(dt='20170602') partition(dt='20170603'); |
2、删除分区:
1 | alter table student_partition1 drop partition (dt='20170601'); |
3、查看分区:
1 | show partitions student_partition1; |
2.2、Hive表的数据导入
2.2.1向表中加载数据
1 | load data [local] impath 'datapath' overwrite | into table student [partition (partcol1=val1,...)]; |
普通表举例:
1 | load data local inpath '/opt/bigdata2.7/hive/person.txt' into table person; |
分区表举例:
1 | load data local inpath '/opt/bigdata2.7/hive/person.txt' into table person partition (dt="20190202"); |
2.2.2通过查询语句向表中插入数据
从指定的表中查询数据结果然后插入到目标表中
1 | insert into/overwrite table tablename select **** from tablename; |
2.2.3、查询语句中创建并加载数据(as select)
1 | create table if not exists tablename as select id,name from tablename; |
2.2.4、创建表时通过location指定加载路径
创建表,并指定在hdfs上的位置
1 | create table if not exists student1(` |
上传数据文件到hdfs对应的目录中
在Linux中运行,注意不是hive端口
1 | hdfs dfs -put /opt/bigdata2.7/hive/student1.txt /usr/hive_remote/warehouse/student1 |
2.2.5、Import数据到指定Hive表中
注意:先用export导出之后,再将数据导入
1 | create table student2 like student1; |
2.3、Hive表的导出
2.3.1、insert导出
1、将查询数据的结果导出到本地
1 | insert overwrite local directory '/opt/bigdata/export/student' select * from student; |
2、将查询结构格式化的导出到本地
1 | insert overwrite local directory '/opt/bigdata/export/student'` |
3、将查询结果导出到HDFS(没有local)
1 | insert overwrite directory '/user/export/student'` |
2.3.2、Hadoop命令导出到本地
1 | hdfs dfs -get /user/hive_remote/warehouse/student/student.txt /opt/bigdata2.7/data |
2.3.3、Hive Shell命令导出
1 | hive -e 'select * from default.student' > /opt/bigdata/data/student1.txt |
2.3.4、export导出到HDFS
1 | export table default.student to '/user/hive/warehouse/export/student1'; |
3. HIve外部表和内部表的区别
创建表时:创建内部表时,会将数据移动到数据仓库指向的路径;若创建外部表,仅记录数据所在的路径, 不对数据的位置做任何改变。
删除表时:在删除表的时候,内部表的元数据和数据会被一起删除, 而外部表只删除元数据,不删除数据。这样外部表相对来说更加安全些,数据组织也更加灵活,方便共享源数据。
1.未被external修饰的是内部表【managed table】,被external修饰的为外部表【external table】。
2.内部表数据由Hive自身管理,外部表数据由HDFS管理。
3.内部表数据存储在hive.metastore.warehouse.dir【默认:/user/hive/warehouse】,外部表数据存储位置由用户自己决定。
4.删除内部表会直接删除元数据【metadata】及存储数据,删除外部表仅仅删除元数据,HDFS上的文件不会被删除。
5.对内部表的修改会直接同步到元数据,而对外部表的表结构和分区进行修改,则需要修改【MSCK REPAIR TABLE table_name】。